The ideal vital substances for your joints
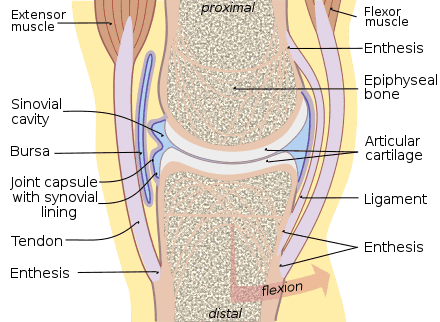
Structure of a joint
Most joints are movable connections between two bones. They consist of the articular surfaces of the bones, which are covered with a layer of cartilage, a fluid-filled joint space and a joint capsule. The joint capsule surrounds the joint and consists of a stable connective tissue envelope. The joint fluid is also called synovial fluid or synovial fluid and helps to “lubricate” and cool the joint. Cartilage is a firm supporting tissue that is elastic in both pressure and bending and perfectly absorbs shocks. Cartilage is not supplied with blood, but absorbs important nutrients from the joint fluid like a sponge with every movement. This clearly explains why exercise on the one hand and a balanced diet on the other are immensely important for joint health. And good joint health is crucial for an active and pain-free life.
Typical diseases of the joints
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a very common disease of the joints and is particularly common in the knee. It is a wear and tear of the cartilage tissue, which can cause symptoms such as pain, stiffness and swelling in and around the affected joints. Osteoarthritis occurs more frequently with increasing age. Osteoarthritis is considered incurable, but there are ways of alleviating the symptoms and slowing down the progression of the disease, even regenerating the damaged cartilage, but this takes time and patience. On the other hand, diet and exercise play an important role. A conscious diet and regular special exercise training, in which muscle stretching is also very important, are the basis for achieving improvements, and taking certain dietary supplements can also help to strengthen the joints. You can find out more in our detailed magazine article “Osteoarthritis”.
Arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammatory process of the joint that can be acute or chronic. Arthritis can affect any joint, a single joint or several. It can be infectious, e.g. caused by bacteria or viruses, or rheumatic, e.g. in the case of rheumatoid arthritis, or it can also be caused by an injury. In arthritis of any cause, the classic signs of inflammation are more or less pronounced. These are redness, swelling, overheating, pain and limited function, and joint effusion may also occur. Acute arthritis caused by pathogens requires medication, e.g. antibiotics. Chronic joint inflammation can be improved with appropriate vital substances. Appropriate exercise training is also very important here.

A joint-friendly diet and suitable nutritional supplements
Good joint health starts with diet and exercise, both of which are important, but here we are focussing on diet and supplements. Only with a balanced diet can our body be supplied with the necessary nutrients, which also helps to keep our joints supple and mobile and prevent complaints. The “cartilage- and bone-active” micronutrients include, for example, vitamins C, D, E and K and the minerals magnesium, calcium, zinc and manganese. These help to build and maintain cartilage and bone tissue and thus prevent complaints in this area. If you already suffer from joint problems, these are the same vital substances that you should pay particular attention to in your diet, and dietary supplements also make sense. There are also some other natural substances that can help you with problems such as osteoarthritis, which you can take in addition to a balanced diet and appropriate exercise training. These are special dietary supplements that can help to promote joint health and reduce discomfort. They contain a combination of different substances such as glucosamine, chondroitin, MSM, manganese and vitamin E. Omega-3 fatty acids, frankincense and turmeric can also be used; what they have in common is that they are said to have anti-inflammatory properties. At kingnature, we develop, produce and distribute natural, scientifically tested food supplements to provide you with the best possible support. Our focus is on quality and care: we attach great importance to an optimised formula, natural cultivation and gentle processing in our own production facility in Switzerland.

A closer look at some substances
Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 is essential for the mineralisation of our bones, it regulates the absorption of calcium and phosphate in the intestine and their incorporation into the bones. The special thing about vitamin D is that we can produce it in our skin, but only with sufficient sunlight. In our latitudes, there is not enough sunlight between October and April to produce the sun vitamin in the skin. According to the FOPH (Federal Office of Public Health), at least half of the Swiss population has a deficiency(Federal Office of Public Health 2012. Vitamin D deficiency: data, safety and recommendations for the Swiss population). Only a small proportion of the vitamin can be absorbed through food; it is contained in small amounts in mushrooms, eggs, cheese, salmon, herring and tuna.
Vitamin K2
Many people do not realise that vitamin K2 is important for the health of bones and cartilage, including joints.
Magnesium
Magnesium is an important mineral in the body and is needed in bones and cartilage, among other things. If the supply is too low, the body draws on its magnesium stores to cover its needs and, among other things, breaks down magnesium from the joints, thereby contributing to joint diseases.
Calcium
It is generally recognised that calcium is important for bones and teeth.
Glucosamine and chondioitin
Glucosamine and chondroitin are natural components of cartilage, the inner lining of the joint and synovial fluid and can help to strengthen them and slow down their breakdown. They can also reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
MSM
MSM (methylsulphonylmethane) is a sulphur compound produced naturally in the body that can also help to reduce inflammation and relieve pain, and can also help to improve joint flexibility. After all, our bodies are made up of 0.2% sulphur, which is around 40 times more than iron.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties and can help to reduce inflammation and pain in the joints.
Frankincense
Frankincense has a long and distinguished tradition in the traditional medicine of many cultures due to its anti-inflammatory properties. Frankincense resin is extracted from Boswellia trees, the Boswellia serrata species has the highest content of the physiologically interesting ingredients, which is why this species in particular is attracting the interest of modern science.
Turmeric
Turmeric, also known as turmeric, has been an integral part of Ayurvedic medicine for a long time. Among other things, the yellow tuber is said to have anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties.
It is important to note that not everyone needs the same nutrients. If you suffer from joint problems or are interested in suitable nutritional supplements to support your joints, you should speak to a specialist in this field to find out which nutrients might be best for you. The correct dosage and duration of use are also crucial.

